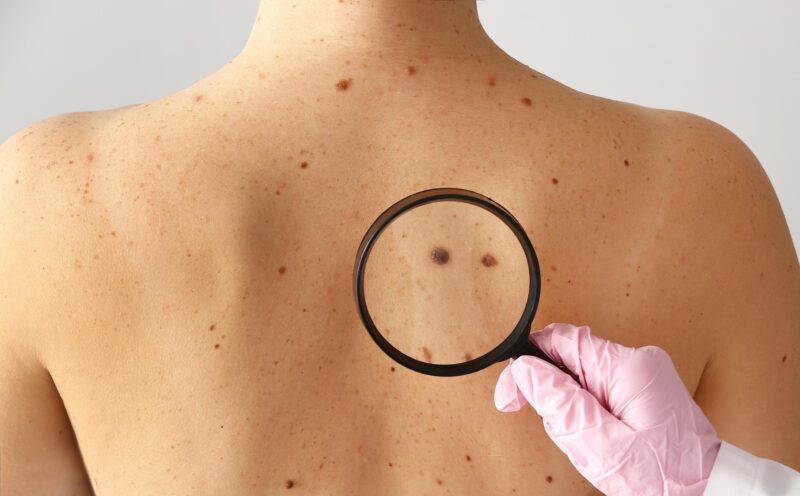
Skin Cancer is a type of disease that occurs when cells in the skin show out of control growth. It occurs when cells get damage often due to exposure of UV rays coming from the sun or tanning beds. This leads to the skin cells to grow rapidly and can form tumours.
Symptoms Of Skin Care
Any new or changing spots on your skin that remain for two weeks or more, that can be a concern and one should show that to a doctor. Skin cancer often shows no symptoms in the early stage.Other key symptoms of Skin Cancer are
1. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) Symptoms:
Pearly or Waxy bump on the skin
A raised, reddish patch one might feels irritated and itching
A sore that bleeds, doesn’t fully recovered
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) Symptoms:
A firm or a bump on sun exposed areas
An open sore or rough patch
3. Melanoma Symptoms:
Changes might occur in the mole
Development of large brown spot
Types Of Skin Cancer
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
It is the most common type of skin cancer. This grows in the basal cells which found in the deepest layer of the epidermis. It looks like a pearly or waxy bump or a sore that bleeds. It doesn’t spread to the other parts of the body and grows slowly. But if it kept unwell there is a risk that surrounding tissues or bones and nerves can damaged.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
It arises from the squamous cells,which makes up most of the upper layers of the skin. This appears like a firm or red nodule. It occurs in sun-exposed parts of the body .It can grow rapidly and has higher chances of spreading.
Melanoma
It develops in the melanocytes; these are the cells that produce melanin, it is the pigment that gives skin its colour. It is the most dangerous type of skin cancer as it can spread in the body very fast. It appears in the body like a dark spot or irregular mole.
Prof Chintamani,Chairman Surgical Oncology Sir Ganga Ram Hospital shared
“Skin cancers range from basal cell carcinoma with good prognosis (outcome) to the other extreme that is malignant melanomas that considered deadly.
The early features of all these cancers would be in the form of a non healing ulcer with added itching, discharge, fixity, and colour change.
Most of these cancers have linked to the exposure to ultraviolet sun rays and absence/ deficiency of protective melanin. Therefore these cancers commonly found in high altitude farmers, Caucasians, and albinos (genetic deficiency of melanin).
Some cancers like basal cell carcinomas ( rodent cell carcinoma) usually occur on the upper part of the face, while melanomas can occur almost anywhere including head and neck, extremities, and trunk. Melanomas usually start as a mole or a naevus. The features of early changes of a mole to melanoma include: itching, increase in size, change in colour, or ulceration. Malignant melanomas are among the deadliest cancers in the body. The naevi that are more commonly involved are junctional. The third common variety i.e. squamous cell carcinomas may have more than one etiological factors.
Any ulcer that is refusing to heal or has started bleeding or has everted edges should raise the suspicion, as these are the common signs of a malignant change in a benign ulcer. Rarely, these cancers present as draining lymph nodes that enlarged.
The HPV related cancers can arise out of common venereal warts and can seen in various parts of the body.”
Dr. Rakesh Kumar Sharma, Head of Department & Senior Consultant Department of Medical Oncology, SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals, Gurugram shared “Let’s understand skin cancer—the abnormal growth of skin cells—and what it signifies. It can be classified into two main categories – melanoma and non-melanoma. The latter includes basal cell skin carcinoma, squamous cell skin carcinoma among other rare versions. When it comes to non-melanoma skin cancer, it most often occurs with increased sun exposure.
As for statistics, skin cancer is among the most diagnose worldwide, compared to other types of cancer, with over 330,000 new cases of melanoma estimated in 2022.
With nearly 60,000 deaths reported, according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), the specialised cancer agency of the World Health Organization. While in India, the reported cases are less than 1% of all cancers, according to a study by GGS Medical College and Hospital in Faridkot, Punjab, the incidence is going up, despite the presence of eumelanin in dark skin, which acts as protection. The reasons given increased exposure to UVB radiation and higher levels of arsenic in drinking water. There is no cause for alarm as one can expect a high success rate when it comes to treatment. However, it recommended to check one’s skin regularly and be on the lookout for early symptoms.
Increased exposure to the sun may lead to non-melanoma skin cancer. For this, it is important to notice any changes in the skin. You can also measure the area and check if it’s growing in size. You, a friend or family member, can take a photo of the exposed area and consult a doctor for expert advice. If you’re spending a lot of time in the sun, it’s a good idea to check for any signs.
If you spot anything suspicious on your skin, be sure to make a doctor’s appointment to rule out the incidence of skin cancer. While the symptoms can vary and even overlap with other conditions,
Here are some signs of Skin Cancer:
● A sore or area that looks unusual; is itchy or bleeds; doesn’t heal or has scabs for over a month
● A sore may also look transparent, pink or even reddish and be rough to touch.
● A small lump that may be growing.
● Red patches that may be itchy.
● Freckles or moles
● A new mole or one that appears different over time.
● Scar-like patches on your skin.
The ABCD rule:
Skin cancer does not look the same for everyone. According to the US National Cancer Institute, the ABCDE rule is a good way to remember what to watch out for:
● Asymmetry: When the shape of one half does not match the other half.
● Border that is irregular: The edges may be ragged, notched or blurred.
● Colour that is uneven: Shades of black, brown and tan, with areas of white, grey, red, pink or blue may be seen.
● Diameter: There is usually an increase in size. Melanomas can be quite small, but most are larger than 6 millimetres wide.
● Evolving: The mole may look different over a few weeks or months.
One can reduce the risk of skin cancer by limiting exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, avoiding sun exposure during peak hours and making it a habit to apply sunscreen regularly. Here are some steps you or your loved ones take to lower the risk:
● Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen of SPF of 30 or higher, to protect against both UV-B and UV-A rays. Apply it at least 30 minutes before you step outside. Use a lip balm too, for better protection.
● Wear sunglasses or caps to protect your face and eyes when you’re exposed to the scorching heat, during the day.
● Protect your arms and legs with long-sleeved tops as well as long trousers or lowers.
● Check your medication and if it makes your skin more sensitive to sun exposure.
● Monitor any skin eruptions for any changes in size or texture and stay alert to any new moles, etc. This includes on your scalp, palms, soles of your feet and between your toes.
Early detection is key to successful skin cancer treatment. When it comes to any cancer, prevention is always better than cure.
Read Also – Delhi-NCR Air Pollution: Ahead of Smog Season, Know What Inhaling Toxic Air Can Do Inside Your Lungs
Conclusion
Skin cancer occurs when the cells get damaged due to UV rays, if one detects it early they can have chances of successful treatment. There is a chance to reduce the risk of skin cancer by minimising the exposure to UV rays, keeping an update on any change that happens to the skin and asking for medical help if one spots anything unusual in the skin. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are one of the most common types of skin cancer whereas melanoma is one of the dangerous types of skin cancer. Adopting protective measures such as less exposure to UV rays or protecting skin by covering it from cloth can protect your skin. Lastly, regular checkup of your skin and consulting a doctor at an early stage if one finds some unusual spot in the skin.