New Delhi:
WHAT IS OCULAR ONCOLOGY?
Eyes can also develop tumours just like other parts of the body. In general terms we describe it as eye cancer. When the healthy cells in or around the eye mutate and grow in numbers rapidly, they form a mass which is called a tumour. Tumours can be benign or malignant. Benign are those that do not have capacity to spread beyond their site of origin and malignant are those which can spread to other organs of the body and can even be life threatening. Eye tumours are threat to eyesight and can even have serious effect on health and life.
Ocular oncology is the speciality that deals with eye tumours. In India around 10,000 new eye cancer cases are diagnosed every year in which between 20-30 % are children and 70 – 80 % are adults. If the cancer is detected at an early stage and with appropriate treatment ,a cure may be possible.
Eye has a unique structure and cancer in the eye can not only potentially wipe out the vision but also can endanger the eye and the life. So the treatment of eye tumour has to be done in a such a way so that the tumour is cured and also the vision and structure is saved.
Oncologist has the knowledge of cancer and the ocular oncologist has knowledge of the eye as well as cancer; thus ocular oncologist is the best choice to treat eye cancer. The treatment in some situations involves team effort of an ocular oncologist, a pathologist,a medical oncologist, a radiation oncologist etc.
PARTS OF THE EYE:-
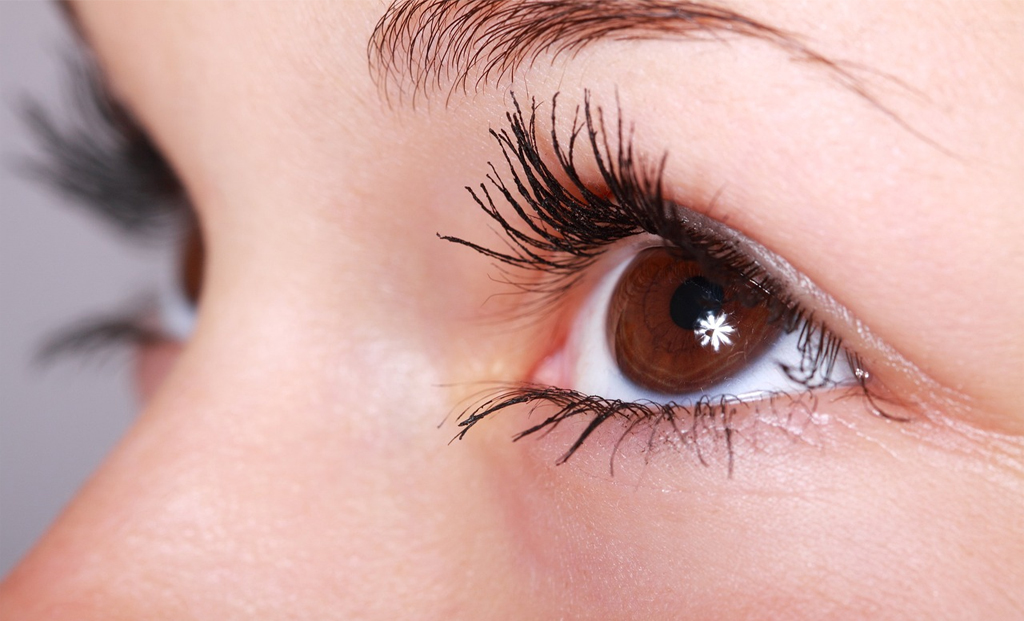
Eye also known as the organ of sight, collects light and sends messages to the brain to form a picture. The main parts of the eye are:
• Eyeball
• Orbit (eye socket)
• Adnexal (accessory) structures, such as the eyelid and tear glands
The outer part of the eye ball is made up of three components sclera, retina, and uvea. The sclera is situated at the outer wall of the eyeball. The retina is made up of thin-layered structure that lines the eyeball and sends information from the eye to the brain. And the uvea nourishes the eye. Retina and uvea contains blood vessels.
The Uvea comprises of three parts: Iris- Its the coloured part of the eye that controls the amount of light entering the eye. Ciliary body- Muscular tissue that produces the watery fluid in the eye and helps the eye focus. Choroid- Its a layer of tissue that is under the retina that has connective tissue and melanocytes, which are pigmented (coloured) cells, and nourishes the inside of the eye. The choroid is the most common site for a tumour inside the eye.
Melanoma is the most common eye cancer that grows grows from structures within the eyes in adults, and Retinoblastoma in children.
Retinoblastoma is most often detected in children younger than six years of age. It starts as a small tumour in the retina and can grow to involve all layers of the eye and even can spread to the brain.
TREATMENT
Treatment depends on the advancement of tumour. Surgery, Radiation and Chemotherapy are the treatment options that help in removing the tumour and its prevention of spread to other part of the body.
An ocular oncologist is the best person to decide on the exact treatment protocol and the person to go to whenever some eye tumor is suspected.
(The writer is Dr. Mahipal Singh Sachdev, Chairman, Centre for Sight Hospital, New Delhi)