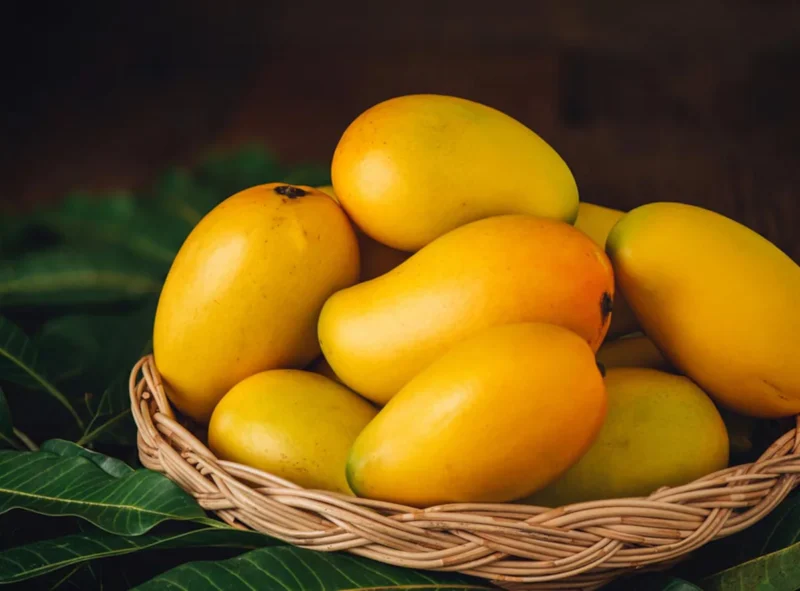
Mangoes are a popular summer treat, loved for their sweet and juicy taste. However, there’s a lingering question about whether eating mangoes can raise blood sugar levels. Let’s explore how mangoes and blood glucose levels relate.
The Nutritional Profile of Mangoes
Mangoes are rich in nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin A, fiber, and antioxidants. They have natural sugars but also contain fiber, which helps slow sugar absorption into the blood. This fiber is essential for managing blood glucose levels.
Blood Sugar: Glycemic Index of Mangoes
The glycemic index (GI) measures how fast food raises blood sugar. Foods with a high GI cause quick blood sugar spikes. Mangoes have a moderate GI, meaning they’re less likely to cause sharp increases in blood glucose compared to high-GI foods.
Impact of Portion Size and Ripeness
How much mango you eat can affect your blood glucose. Eating too much of any fruit, including mangoes, can raise blood sugar. Riper mangoes are sweeter and might have more sugar than less ripe ones.
Eating Mangoes With High Blood Sugar Levels
Mangoes can be a tasty and healthy part of your diet if eaten in moderation. Pair mangoes with protein, healthy fats, and fiber-rich foods to help manage their effect on blood glucose.
Suffering from Blood Sugar?
The effect of mangoes on blood glucose varies by person. Factors like metabolism, diet, and activity level all play a role in how your body handles the sugars in mangoes.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals
If you are worried about how mangoes might affect your blood glucose, talk to a healthcare professional or dietitian. They can give personalized advice based on your health needs and help you decide the best way to enjoy mangoes.
Mangoes are a delicious and nutrient-filled fruit, but their effect on blood glucose depends on factors like portion size, ripeness, and individual metabolism. By eating mangoes in moderation and as part of a balanced diet, you can enjoy them while keeping your blood sugar stable.