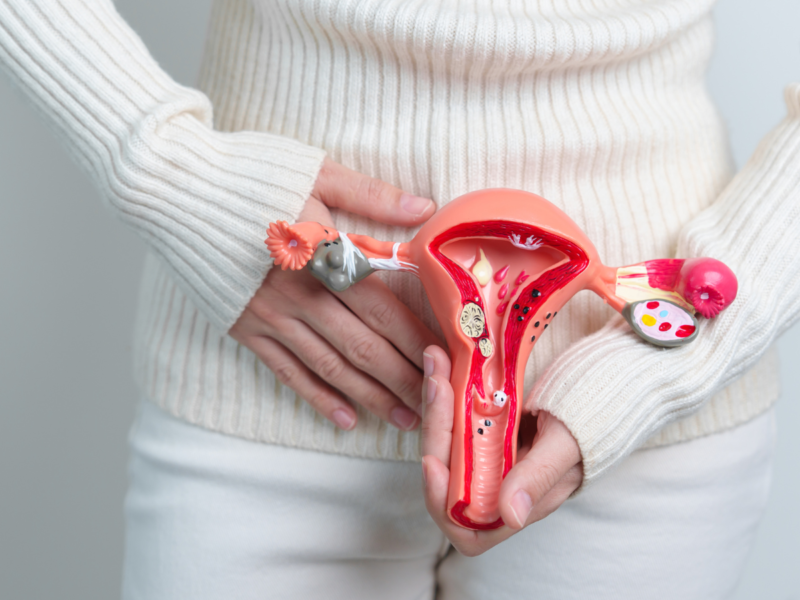
New Delhi, 28 November 2024: A recent study in the United States has shown a significant drop in cervical cancer deaths among young women, marking a remarkable achievement in the fight against this preventable disease. The study, which analyzed trends in cervical cancer mortality over the past few decades, highlights the effectiveness of early detection methods, the widespread adoption of the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, and improvements in healthcare access. These findings provide hope for further reductions in cervical cancer-related deaths, particularly among younger generations.
Study Overview: Key Findings from the Research
Researchers from the National Center for Health Statistics discovered that between 2019 and 2021, only 13 women under the age of 25 died from cervical cancer, a stark contrast to 35 deaths recorded between 2013 and 2015. This notable change highlights the effectiveness of preventive measures in reducing mortality rates among young women. The researchers point out that this is the first study explicitly linking the HPV vaccination to a decrease in cervical cancer deaths for this age group.
Understanding HPV and Its Role in Cervical Cancer
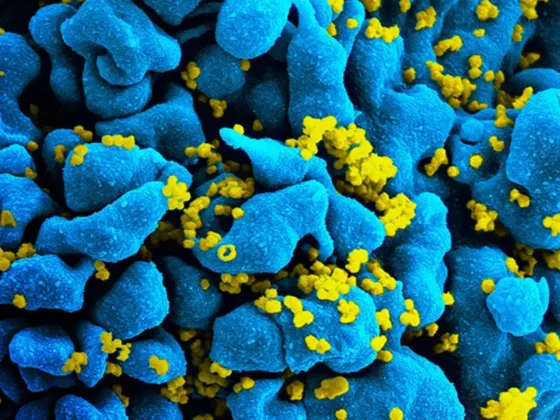
The human papillomavirus (HPV) is a collection of viruses, some of which can lead to cervical cancer. As the most common sexually transmitted infection, high-risk strains of HPV are known to be the main cause of cervical cancer. The HPV vaccine works to prevent these infections, consequently lowering the chances of developing cervical cancer. The introduction of this vaccine has been revolutionary in public health, especially for young women who face a higher risk of cervical cancer later on.
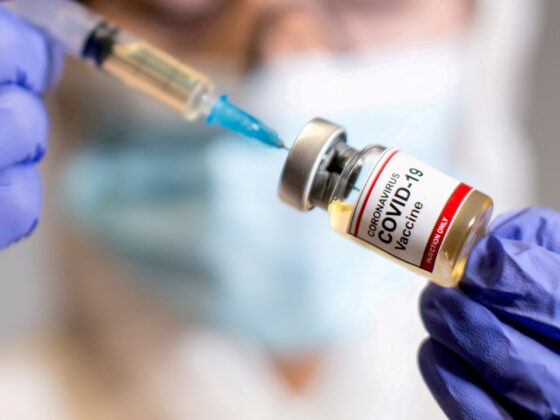
The Importance of Vaccination: A Public Health Success Story
Since its launch in 2006, the HPV vaccination program has played a vital role in reducing cervical cancer rates. The vaccine has been made available to both boys and girls, with the aim of achieving herd immunity to protect future generations. The recent study results serve to underscore the success of this initiative, as the vaccine not only prevents HPV infections but also significantly lowers the risk of developing cervical cancer. Public health officials continuously advocate for higher vaccination rates to further decrease the incidence of this disease.
Challenges and Barriers to Vaccination
Despite these encouraging trends, obstacles remain in boosting vaccination rates. Issues like misinformation about the HPV vaccine, healthcare accessibility, and cultural attitudes towards vaccination can impede efforts to protect young women against malignant cervical tumour. Health authorities are working to overcome these challenges through educational outreach, highlighting the safety and effectiveness of the HPV vaccine.
Future Implications: Continuing the Fight Against Cervical Cancer
While the reduction in cervical cancer deaths among young women is promising, it is essential to keep the momentum going. Ongoing research and monitoring of malignant cervical tumour rates are fundamental to understanding the long-term impacts of the HPV vaccination. Moreover, continuous education efforts are vital to ensure that parents and young women recognize the importance of obtaining the vaccine to prevent malignant cervical tumour.