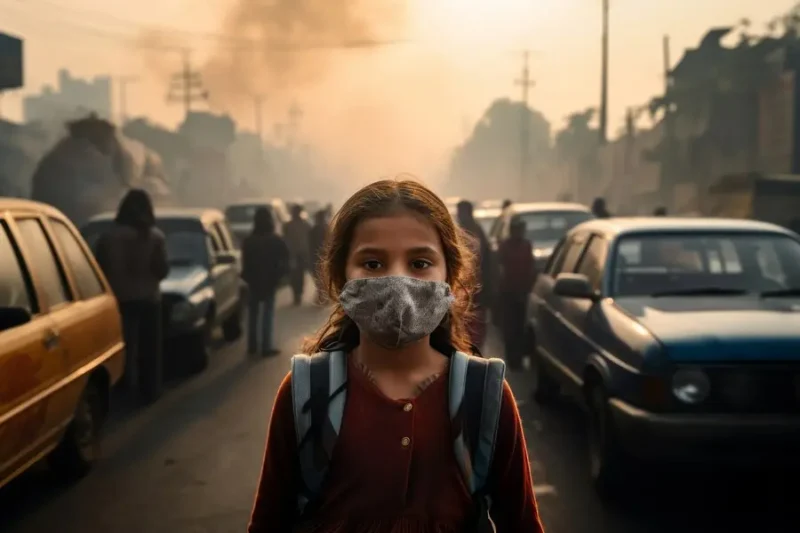
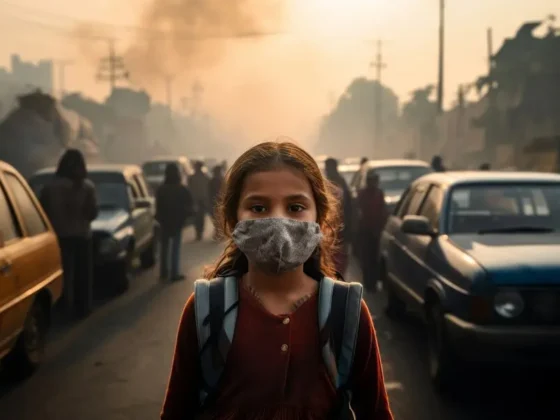
New Delhi, 09 November 2024: Air pollution has quietly become a significant factor in the increasing number of lung cancer cases around the globe. So, what’s behind this alarming trend? For starters, the air we breathe is filled with harmful substances that can lead to cancer. Prolonged exposure to these pollutants not only contributes to chronic respiratory diseases but is also worsened by the rapid urbanization we have witnessed. Certain groups, like children and the elderly, face even greater risks. To tackle this issue effectively, we must first grasp the connection between air pollution and lung cancer, paving the way for stronger policies and health practices.
The Role of Air Pollution in Lung Cancer Development
Our atmosphere is a cocktail of dangerous substances, including fine particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and volatile organic compounds. Among these, PM2.5 – particles so small they can infiltrate our lungs and bloodstreams – is particularly concerning. Studies have found that individuals exposed to these carcinogens over a long period are at a significantly heightened risk for lung cancer.
Chronic Respiratory Diseases as a Precursor
Conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma are often made worse by polluted air. Those already battling these illnesses generally have weaker lung function, which puts them at a greater risk for lung cancer. The inflammation that these diseases cause creates conditions where cancer cells are more likely to thrive, reinforcing the connection between our air quality and cancer risks.
Urbanization and Its Impact on Air Quality
As cities grow, so does the pollution stemming from vehicles, industries, and construction. Urban areas often are the most problematic when it comes to air quality, with significant emissions contributing to the deterioration of our air. Studies reveal that those living in crowded cities face a higher chance of developing lung cancer due to constant exposure to polluted air.
Vulnerable Populations at Greater Risk
Some groups are disproportionately affected by poor air quality. Children, with their developing lungs and immune systems, are particularly at risk from harmful air pollutants. Similarly, older adults may have underlying health issues that become exacerbated in polluted environments, increasing their likelihood of developing lung cancer. This highlights the urgent need for focused strategies to safeguard these vulnerable populations.
The Need for Awareness and Regulation
Despite mounting evidence linking air pollution to lung cancer, many people still lack a clear understanding of the dangers tied to bad air quality. There is an urgent need for education campaigns to raise awareness about the health risks posed by air pollution and the critical need to monitor environmental conditions.
Regulatory Measures and Their Importance
Governments are fundamental in enforcing standards for air quality. Stricter controls on emissions from cars and industries can significantly cut pollution levels. By fostering clean energy initiatives and promoting sustainable city planning, we can improve the overall state of our air. Collective prioritization of air quality regulations is essential to protect public health and lower the lung cancer incidence associated with air pollution.
The link between air pollution and lung cancer is undeniably complex but critical. As air quality continues to decline, so does our health, especially for those who are most at risk. It’s vital for individuals, communities, and governments to unite and fight against this pressing health crisis. By boosting awareness, enforcing stricter regulations, and encouraging cleaner air initiatives, we can strive to reduce the negative impact of air pollution on lung cancer rates and safeguard the health of future generations.