Dr. Bhupesh Kumar Neurologist- Neuro and Pain Care Clinic.
A head injury is any trauma to the scalp, skull, or brain. The injury may be only a minor bump on the skull or a serious brain injury. Head injury can be either closed or open (penetrating). A closed head injury means you received a hard blow to the head from striking an object, but the object did not break the skull.
What are some causes of head injury?
Head injury defines a vast array of injuries that can occur on the scalp, skull, brain and/or underlying tissue and blood vessels of the brain, the damage ranges from mild to severe even leading to death. Head injuries commonly are known as TBI (Traumatic Brain Injury) or Brain Injury in the medical world. The injury can be as mild as bump, bruise (contusion), or cut on the head. Head injury can be either closed or open Closed Head injury means someone received a hard blow to the head from striking an object but the object did not break open the skull.
Open or Penetrating head injury means you were hit with an object that broke the skull and entered the brain, such as in a car accident, gunshot to the head or going through the windshield during a car accident.
Q2. Types of head injuries?
Head injuries can be classified into the following:
- Concussion – Concussions means instant loss of awareness, consciousness or alertness for a few minutes up to a few hours following a traumatic event such as a soccer ball hitting on your head hard, or a cricket ball or sudden fall on the ground.
- Skull fracture – as the name suggests, the skull is broken by an external object may be a rod hitting on the head and breaking the skull or an object hitting on the head and breaking the skull and entering or not entering the brain.
- Intracranial Hematoma/haemorrhage- Intracranial hematoma means that there is blood in or around the brain causing it to swell and increasing the pressure on the brain, this type of head injury can range from mild to life threatening, as our brain is sitting around in a tight environment (the skull) so any sudden ICH can increase the pressure in the brain (Intracranial pressure) and can force the brain to have midline shift inducing serious complications even involving surgeries.
Q3. What injuries can be given first aid?
Depending on the type of injury, treatment may include:
- Putting an ice pack on the head (in a case of very mild head injury followed by a consultation with a neurologist)
- Rest
- Bandage on the area of wound
- Observe the patient for any signs of convulsions(seizures), vomiting or nausea.
If the head injury is moderate or severe then immediate medical attention to the patient should be given by calling an ambulance or taking the patient to the nearest hospital.
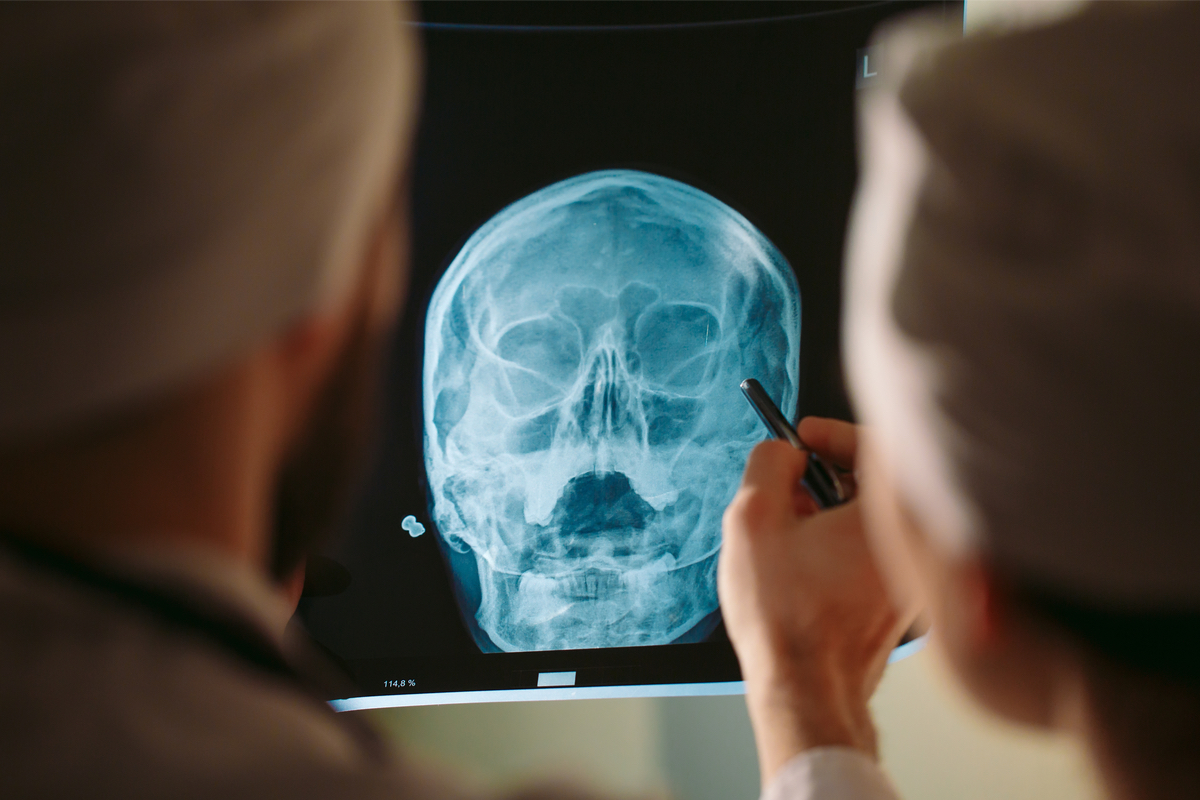
Treatment or first aid can be decided on the bases of the extent of injury, if the patient has a severe head injury, they will require monitoring and observation in the hospital for increased intracranial pressure followed by a Head CT (NCCT) to check for any signs of ICH. Since the brain is covered by the skull, there is only a small amount of room for it to swell, this causes pressure inside the skull to increase that can eventually lead to brain damage.
Q4. When to seek immediate medical help for a head injury?
Depending on the extent of the injury medical attention is decided for head injuries for instance, if the patient has met with an accident and has severe head injury immediate medical attention is required, but if a sports player had a sports injury where in an object touched their head then they should be observed first with a help of a neurologist who can guide them to necessary medical attention.
Q5. First Aid Remedies in case of a head injury?
As explained earlier head injury can range from mild to life-threatening, the best you can do is to check for the following signs when a person has received a head injury:
- Stop any bleeding by firmly pressing a clean cloth around the wound, ensure that your hands are sanitised before touching the wound else that would risk infection.
- If the injury is serious be careful not to move the person’s head, if the blood soaks through the cloth do not remove it, put another on top of it and call an ambulance immediately.
- Ensure enough airway is given to the patient and do not crowd the patient.
- If the person is vomiting, to prevent choking, roll the person’s head, neck, and body as one unit onto their side. This still protects the spine, which you must always assume is injured in the case of a head injury. Children often vomit once after a head injury. This may not be a problem, but call a doctor for further guidance.
5. Apply ice packs to swollen areas (cover ice in a towel so it does not directly touch the