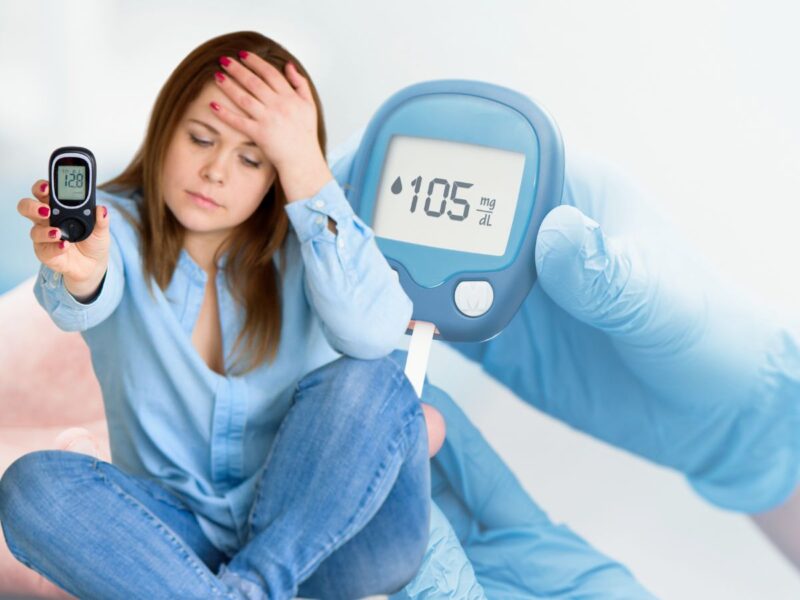
New Delhi, 15 November 2024: India is currently grappling with a serious health crisis, marked by an alarming rise in diabetes cases. Recent reports show that the country has surpassed even China, becoming home to the highest number of diabetics globally. This concerning trend prompts several critical questions: What is fueling the prevalence of diabetes in India? Why is there resistance to necessary lifestyle changes? What hurdles does the healthcare system face in addressing this issue? Why is there a lack of awareness about diabetes? And most importantly, how can we effectively tackle this epidemic? Understanding these elements is vital for combating this growing health challenge.
The Diabetes Epidemic in India
The diabetes situation in India is multifaceted, influenced by genetics, lifestyle choices, and eating habits. The International Diabetes Federation reports that around 77 million people in India are living with diabetes—a figure expected to rise dramatically in the years ahead. This alarming statistic underscores the urgent need for public health initiatives and awareness efforts to confront this crisis head-on.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Diabetes
A major contributor to India’s diabetes prevalence is the rapid shift in lifestyle and eating habits. As urbanization increases, there’s a growing tendency to consume processed foods rich in sugars and unhealthy fats, leading to obesity—a significant risk factor for diabetes. Furthermore, sedentary lifestyles are becoming commonplace, with many embracing desk jobs that encourage minimal physical activity. These lifestyle shifts have created an environment conducive to the rise of diabetes.
Genetic Predisposition and Cultural Influences
Genetics also significantly influences the diabetes epidemic. Research indicates that those of South Asian descent have a genetic predisposition to insulin resistance, which can contribute to the development of Type 2 diabetes. Additionally, traditional diets and cultural practices, while flavorful, often lead to high carbohydrate intake, further increasing diabetes risk. Recognizing these genetic and cultural elements is essential for developing effective prevention strategies.
Lack of Awareness and Education
Despite the increasing number of diabetes cases, awareness surrounding the disease is surprisingly low in India. Many individuals lack knowledge of risk factors, symptoms, and potential complications linked to diabetes. This gap in understanding can result in late diagnoses and inadequate disease management. Hence, education and awareness efforts are crucial to informing the public about diabetes, its ramifications, and the necessity for early detection and lifestyle adjustments.
Healthcare access presents another significant obstacle in effectively managing diabetes. In rural regions, healthcare facilities are often scarce, meaning many people lack access to vital services such as regular check-ups and screenings for diabetes. Moreover, there is a deficiency of trained healthcare professionals specializing in diabetes care. Overcoming these healthcare barriers is critical to enhancing diabetes management and patient outcomes.
Government Initiatives and Public Health Policies
In light of the diabetes crisis, the Indian government has launched several public health initiatives aimed at prevention and management. Programs that focus on lifestyle changes, awareness, and screening have been introduced, yet their implementation and reach require bolstering. Working collaboratively with local communities and healthcare providers is key to improving the success of these initiatives.
The Role of Technology in Diabetes Management
Technological advancements are playing a pivotal role in managing diabetes. With the growing availability of mobile health apps, wearable devices, and telemedicine, individuals can easily track their blood sugar levels and access timely medical guidance. These innovations empower patients to take charge of their health and make informed lifestyle choices.