Multiple sclerosis (MS) is generally considered an autoimmune condition that affects the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system. The disease affects women more often than men.
According to the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, women may be up to three times likelier than men to get MS. The disease can also cause symptoms specific to women. But women and men share most of the same symptoms of MS.
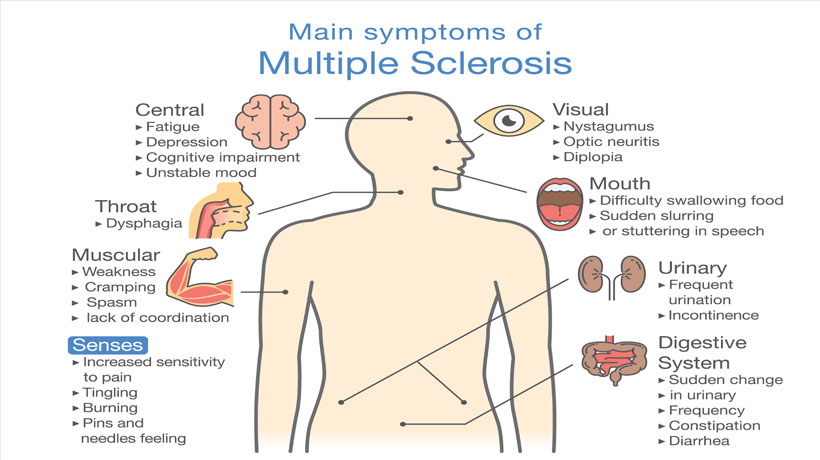
MS symptoms that affect both women and men
In general, MS symptoms are the same for both women and men. But the symptoms vary for everyone depending on the location and severity of nerve damage caused by inflammation.
Some of the most common MS symptoms are listed below.
Muscle symptoms
In MS, the body’s immune cells attack the nervous system. This can occur in the brain, spinal cord, or optic nerves. As a result, MS patients can experience muscle-related symptoms which include:
muscle spasms
numbness
balance problems and lack of coordination
difficulty moving arms and legs
unsteady gait and trouble walking
weakness or tremor in one or both arms or legs
Eye symptoms
Vision problems can occur in both men and women with MS. These can include:
vision loss, either partial or complete, which often occurs in one eye
pain when moving your eyes
double vision
blurred vision
involuntary eye movements
more generalized eye discomfort and visual difficulties
All of these eye symptoms are due to MS lesions in the part of the brain that’s responsible for controlling and coordinating vision.
Bowel and bladder changes
Both bladder dysfunction and bowel symptoms occur frequently in MS. Dysfunction in the pathways of the nervous system that control your bladder and bowel muscles cause these problems.
Possible bladder and bowel symptoms include:
trouble starting to urinate
frequent urge or need to urinate
bladder infections
urine or stool leakage
constipation
diarrhea