During his entire career Xiang-Dong Fu, PhD, has never been more excited about something. He has long studied the basic biology of RNA, a genetic cousin of DNA, and the proteins that bind it.
But a single discovery has launched Fu into a completely new field: neuroscience.
Over a decade, Fu and his team at University of California San Diego School of Medicine studied a protein called PTB, which is well known for binding RNA and influencing which genes are turned “on” or “off” in a cell.
In order to study the role of a protein like PTB, scientists often manipulate cells to reduce the amount of that protein, and then watch to see what happens.
Several years ago, a postdoctoral researcher working in Fu’s lab was taking that approach, using a technique called siRNA to silence the PTB gene in connective tissue cells known as fibroblasts.
But it’s a tedious process that needs to be performed over and over. He got tired of it and convinced Fu they should use a different technique to create a stable cell line that’s permanently lacking PTB. At first, the postdoc complained about that too, because it made the cells grow so slowly.
But then he noticed something odd after a couple of weeks — there were very few fibroblasts left. Almost the whole dish was instead filled with neurons.
In this serendipitous way, the team discovered that inhibiting or deleting just a single gene, the gene that encodes PTB, transforms several types of mouse cells directly into neurons.
More recently, Fu and Hao Qian, PhD, another postdoctoral researcher in his lab, took the finding a big step forward, applying it in what could one day be a new therapeutic approach for Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases.
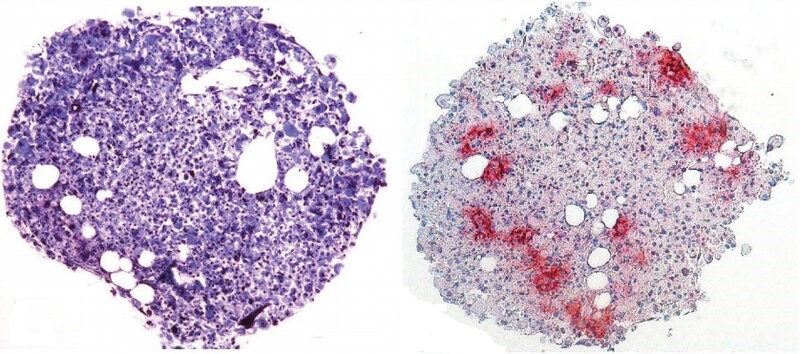
Just a single treatment to inhibit PTB in mice converted native astrocytes, star-shaped support cells of the brain, into neurons that produce the neurotransmitter dopamine.
As a result, the mice’s Parkinson’s disease symptoms disappeared.
The study is published June 24, 2020 in Nature.
“Researchers around the world have tried many ways to generate neurons in the lab, using stem cells and other means, so we can study them better, as well as to use them to replace lost neurons in neurodegenerative diseases,” said Fu, who is a Distinguished Professor in the Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine at UC San Diego School of Medicine.
“The fact that we could produce so many neurons in such a relatively easy way came as a big surprise.”
The researchers developed a noninfectious virus that carries an antisense oligonucleotide sequence — an artificial piece of DNA designed to specifically bind the RNA coding for PTB, thus degrading it, preventing it from being translated into a functional protein and stimulating neuron development.
Antisense oligonucleotides, also known as designer DNA drugs, are a proven approach for neurodegenerative and neuromuscular diseases — study co-author, Don Cleveland, PhD, pioneered the technology, and it now forms the basis for a Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved therapy for spinal muscular atrophy and several other therapies currently in clinical trials.
Cleveland is chair of the Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine at UC San Diego School of Medicine and member of the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, San Diego.