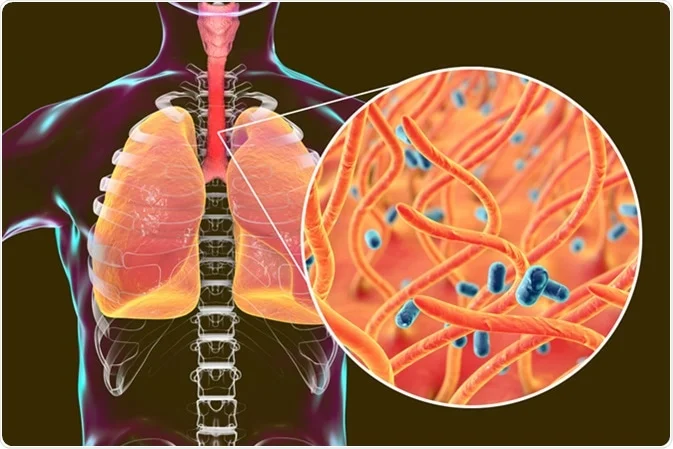
Whooping cough is making a comeback! In the latest report, authorities have confirmed that another baby has died from an infection of whooping cough, bringing the total number of deaths of infants in England since the outbreak began to 10, officials at the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) said.
This death coincides with recent UKHSA data showing that confirmed laboratory cases of whooping cough in England topped 10,000 in this year. While most cases are in people aged 15 or older, more than 300 have been in babies under three months – the most at-risk group from the infection.
It is believed that the outbreak started in England last November, and 10 infant deaths have now been confirmed. The first death was reported in December 2023, and the rest occurred between January and June 2024.
According to reports, Whooping cough is making a comeback in several parts of the world, with deaths reported in China, the Philippines, Czech Republic and the Netherlands, and outbreaks in countries including the US and UK.
What is Whooping Cough?
Whooping cough affects the respiratory system, especially the lungs and airways. The name comes from the distinctive ‘whoop’ sound made by those infected when they try to breathe after a coughing spell. This infection is particularly hazardous for infants and young children, potentially leading to severe complications or even death if untreated.
Symptoms of This Disease
- Persistent Coughing: A persistent cough is a primary symptom, often severe and lasting several weeks. This can cause significant discomfort and fatigue, with coughing fits worsening at night.
- ‘Whoop’ Sound: The signature ‘whoop’ sound following a coughing fit indicates whooping cough. This high-pitched sound occurs as the individual struggles to inhale deeply after coughing.
- Post-Cough Vomiting: Severe coughing fits can sometimes lead to vomiting, adding to the affected person’s discomfort and weakness.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Chronic coughing and related symptoms often result in fatigue and weakness, affecting daily activities and overall quality of life.
Prevention of This Disease
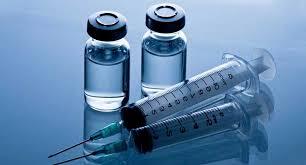
- Vaccination: Vaccination is the most effective prevention method. Vaccines like the DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis) vaccine are routinely administered to infants and young children to protect them from pertussis.
- Boosters for Adolescents and Adults: Adolescents and adults should receive booster shots to maintain immunity. This is crucial for those in close contact with infants and young children.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Good hygiene practices, such as regular hand washing and covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, can help prevent the spread of whooping cough. Avoiding close contact with infected individuals is also key.
- Stay Informed: Being aware of whooping cough symptoms and seeking medical attention promptly if you suspect an infection is crucial. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and reduce the disease’s spread.
Whooping cough is a serious respiratory infection that demands attention and preventive actions. By recognizing symptoms and prioritizing vaccination and hygiene, we can mitigate this disease’s impact on public health. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and prioritize your health and that of your community.