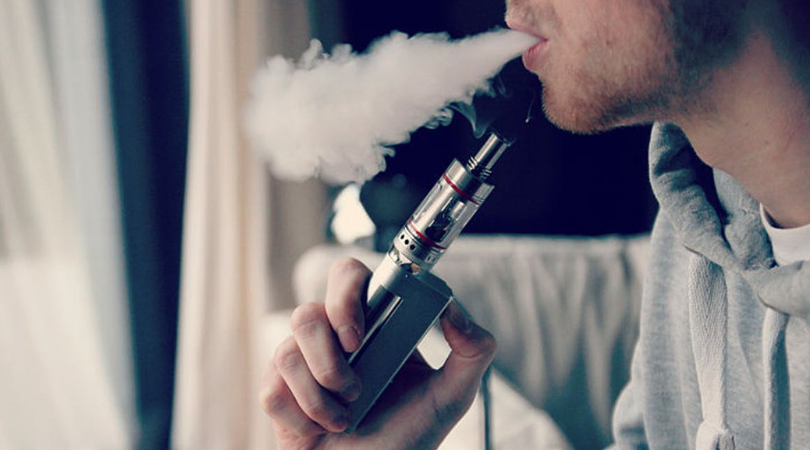
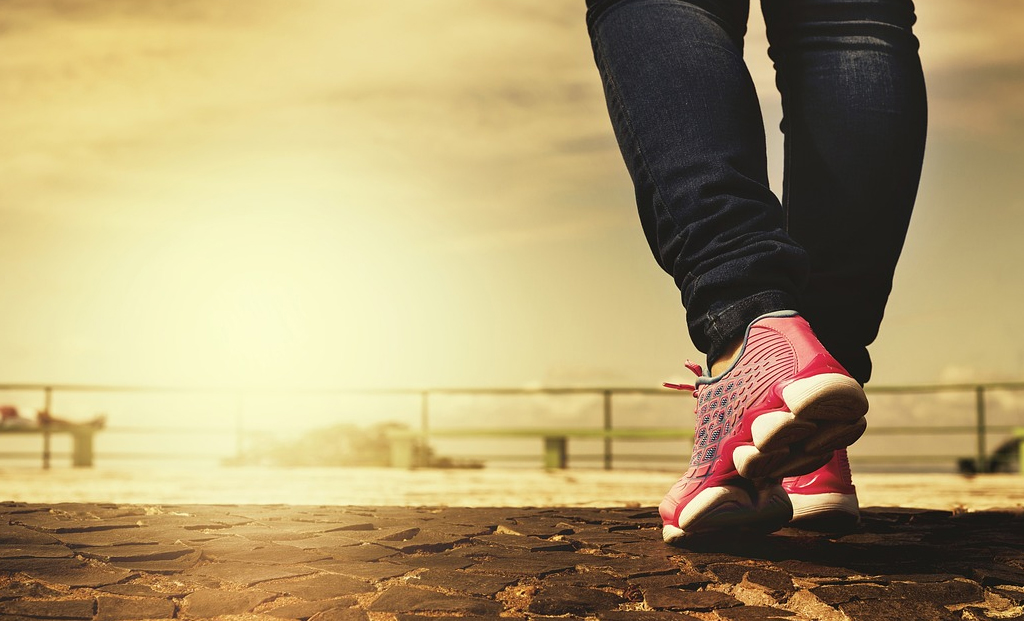
E-cigarettes, also popularly known as vape or JUUL, are battery operated electronic cigarettes which emits doses of vaporized nicotine or non-nicotine solutions for users to inhale. They first appeared in Chinese markets in 2014 and since then has been a rage among youngsters, “vaping” has become one of the most popular form of tobacco use among the teens in the west.
Even though earlier e-cigarettes were considered less harmful than normal cigarettes it has been found that in the recent years vapes or JUULs have 5% nicotine pods which makes it as bad as smoking a full pack of cigarettes. This ends up giving the user more exposure in a very small amount of time making It easier for the users to get addicted to nicotine.
While nicotine addiction is an obvious side effect of “vaping”, chronic nicotine exposure can lead to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Inhaling nicotine also leads to increase in heart rate and blood pressure. E-cigarettes are also being called the gateway for smoking traditional cigarettes and possible consumption of other drugs. Flavoured e-cigarettes may pose another health threat, they often contain a chemical compound called diacetyl, which is associated with a rare lung disease called bronchiolitis obliterans that causes permanent damage to the bronchioles, the tiniest airways in the lungs
12 states in India have already banned the selling and usage of e-cigarettes following an advisory from the health and family welfare issued last year. Even though India has the second largest population of smokers in the world, e-cigarettes had to be banned as they were easily accessible to the younger crowd and would introduce a whole new generation to smoking at a very young age.