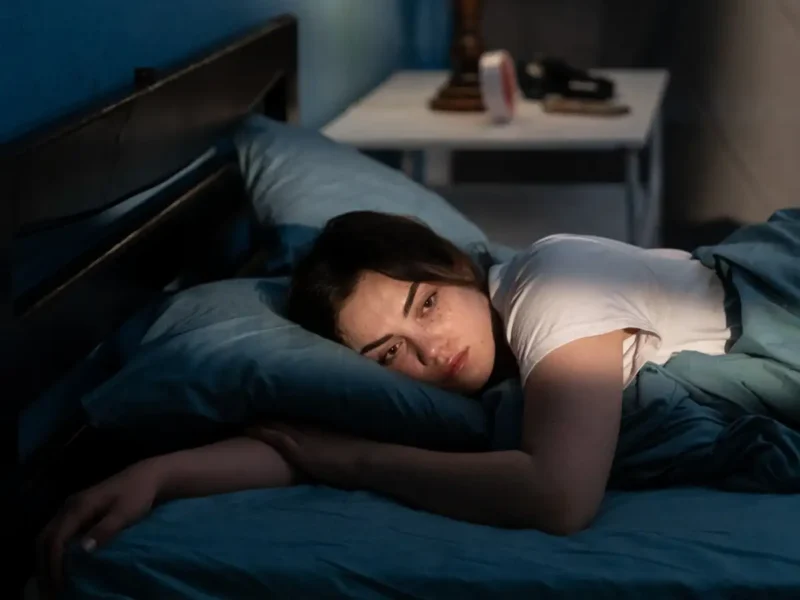
New Delhi, September 12: Sleep is a vital component of overall health. And disruptions to sleep patterns have linked to various health issues. Recent studies have highlighted a concerning association between late-night sleep and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This article will explore the scientific evidence supporting this connection and discuss strategies for improving sleep quality and reducing the risk of diabetes.
The Link Between Sleep and Diabetes
Numerous studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between sleep disturbances and the development of type 2 diabetes. Late-night sleepers, in particular, have found to be at a significantly higher risk. Several factors may contribute to this association:
Hormonal imbalances: Sleep plays a crucial role in regulating hormones that control blood sugar levels, including insulin and cortisol. Disruptions to sleep can lead to hormonal imbalances, making it more difficult to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Increased inflammation: Chronic sleep deprivation associated with increased inflammation in the body. Which can contribute to insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes.
Altered metabolism: Poor sleep quality can disrupt metabolic processes, leading to weight gain and other factors that increase the risk of diabetes.
Lifestyle factors: Late-night sleepers are more likely to engage in unhealthy behaviors, such as eating unhealthy foods and consuming excess caffeine, which can contribute to diabetes risk.
The Impact of Late-Night Sleep on Diabetes Risk
Research has consistently shown that individuals who regularly go to bed late are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes compare to those who sleep earlier. Studies have found that even a modest shift in sleep timing, such as going to bed an hour later, can increase the risk of diabetes by up to 50%.
How To Manage Your Sleep To Stay Safe From Diabete?
To reduce the risk of diabetes, it is important to prioritize sleep quality and establish a consistent sleep schedule. Here are some strategies that can help:
Create a sleep-conducive environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool.
Stick to a consistent sleep schedule: Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends.
Limit screen time before bed: The blue light emitted by electronic devices can interfere with sleep. Avoid using screens for at least an hour before bed.
Avoid stimulants: Limit your intake of caffeine and alcohol, especially in the evening.
Manage stress: Chronic stress can disrupt sleep. Practice relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing to manage stress.
Regular exercise: Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality, but avoid intense workouts close to bedtime.
Read Also – Babesiosis, a Tick-Borne Illness, On The Rise in US: Here’s All You Need to Know
The link between late-night sleep and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes is well-establish. As per experts, to avoid the blood sugar fluctuations, one needs to prioritize their sleep quality and adopt healthy sleep habits. It is essential to make sleep a priority in your daily routine to protect your overall health and well-being.